Cold weather Concrete placement and its important point
Cold weather Concrete placement
It is true that concrete is widely used in modern construction, but it is not a perfect material! In addition to high weight, concrete is vulnerable to air temperature. While concrete placement can be done at any time of the year and almost anywhere, there is an ideal temperature range for concrete placement. If concrete placement is done in cold weather, special measures must be taken to implement it so that the overall health of the concrete is not endangered in the short and long term. Join us to delve deeper into the topic of cold concrete placement.
Hydration and concrete temperature in cold weather
Aggregates (Gravel and sand) and cement paste made from a mixture of water and cement, which contain all the constituents of concrete. When cement paste and aggregate are mixed together, it forms a flexible material that can be poured in place to form the desired mold. Then, after a while, it becomes a heavy, resistant and hard mass.
Concrete is known by a process called hydration. Hydration, which is the same as water-cement mixture, guarantees the final strength of concrete. During this process, the compounds in the cement react with the water and crystallize, and in terms of chemical reaction, separate the cement particles together, resulting in a hard product.
The initial hardening process takes place during the first few days after concrete placement, but the concrete curing process continues for many years thereafter. That is why it is said that concrete strengthens over time. Cold air can cause problems in the process of hydration and setting of concrete, but analysis of this issue requires engineering knowledge.
At temperatures above zero ° C, the development of strength in fresh concrete is very slow. If the ambient temperature drops below zero degrees, some of the water in the concrete may freeze. The setting stops until the chemical reaction is completed, and this cessation of hydration increases the porosity and decreases the strength and durability.
Concrete placement problems in cold weather
The ninth article in the National Building Code states: “Concrete placement for cold weather is a period when the average daily ambient temperature is below 5 degrees Celsius for more than 3 consecutive days. The average daily temperature is the average of the highest and lowest temperatures during the period from midnight to midnight the next day. “When temperatures above 10 degrees Celsius occur in more than half of the 24-hour period, it is no longer considered cold air.”
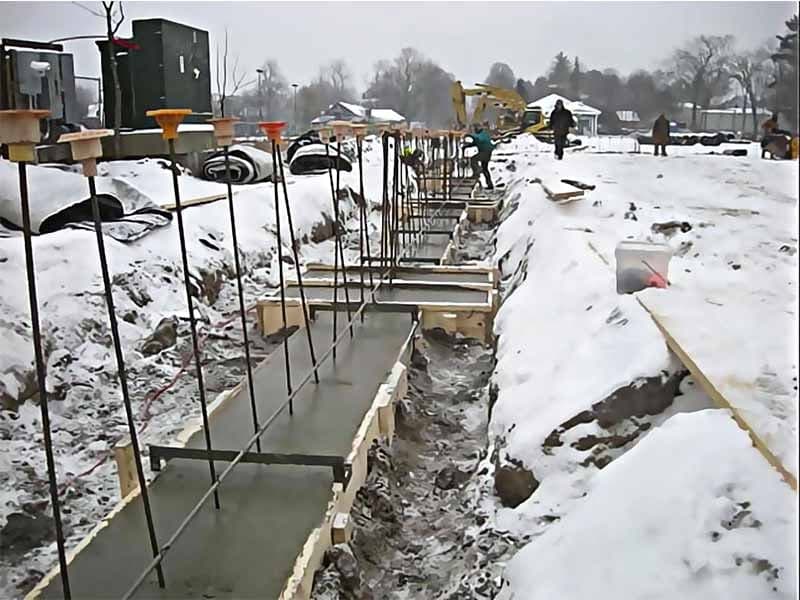
The first three days after concrete placement are crucial. During this time, the semi-liquid concrete hardens and performs most of its function by bonding the cement with water. Because the presence of water is very important for the curing process, concrete placement in winter causes many problems.
In the season when the temperature may drop below zero, the ratio of water to cement and the percentage of aggregates can change. At low temperatures, freezing of water in the concrete mix leads to problems that pose a potential risk to the project. In cold weather, concrete cannot be placed on site without additional preparation and equipment!
Low temperature and freezing hazards of concrete
The hydration process that hardens the concrete involves a chemical reaction that is affected by heat. Although the excessive heat of summer can negatively affect the performance of concrete, the low temperature in winter will cause more damage to the concrete.
At temperatures below 40 degrees Fahrenheit, the initial setting process can take more than 2 to 24 hours, and in very severe weather conditions, this time can be much longer. At this time, the concrete placed at freezing temperatures can cause problems with freezing and expansion of the water inside the mixture.
These problems often include flaking (that is, flaking of the polished surface) and crushing of concrete members under the weight of the building. Concrete placement in cold weather may prevent the concrete from hardening in normal times and cause numerous structural defects. For these reasons, concrete placement in the cold seasons of the year is usually done by professionals who know what precautions to take.
Solutions and requirements for concrete placement in cold weather
If the area is very cold, chemical accelerators that speed up the curing process can be added to the concrete mix before placement. Hot concrete mixes and cement mixes that are specific to frozen environments can be used in a variety of applications.
Here are some tips and techniques for concrete placement in cold weather:
1.Reducing the permeability of concrete:
Of all the factors affecting the frost resistance of concrete, permeability plays the most important role. Impermeable concrete has only a small amount of free moisture in its pores, and therefore the destructive function of freezing and expanding water is largely eliminated.
There are three basic ways to reduce the permeability and thus increase the cold resistance of concrete, which include the following:
- The use of bubble additives prevents the movement of capillaries in the concrete.
- Reducing the water-to-cement ratio and using lubricants in turn reduces the rate at which the concrete bleeding
- The use of Pozzolans such as fly ash to replace part of the cement (generally fifteen to twenty percent) can reduce the permeability of concrete.
2- Early strength of concrete:
: The rate of increase of concrete strength at low temperatures is relatively low and this can affect the speed of construction. Methods of achieving faster setting times and early strengths of concrete differ with specific applications. To overcome this problem, there are several ways to produce early resistance
- Use of accelerator additives
- Use hot water in concrete mix
- Cover or heat the molds before placement
Despite the problems that can arise during the concrete placement process, concrete placement in cold weather can still be an effective process if the basic measures and requirements are followed. First, the place where the concrete is placed must be prepared.
Project managers often use thermal mats to heat the molds to a more stable temperature, and then use a special concrete blanket to cover and keep the concrete mix warm for the first few days.
3- Increase the amount of cement
In some projects, people use a combination of Portland cement types I and II. Other people may use Type III cement, which is cement with high early strength. This cement is finer and has a faster hydration reaction. Therefore, the increase in early compressive strength of concrete made with type III cement is greater. The amount of use of each of these cements must have an economic justification for the project
Concrete Curing in Cold Weather
According to the ABA Regulations and Article 9 of the National Regulations, the application of fresh concrete must continue for at least 24 hours until it reaches strength of 50 MPa. The following methods can be used to operate fresh concrete and protect it from freezing:
- Use of protective insulation coating
- Heating concrete using electric heaters or hot water spraying on concrete members
- Other methods approved by the monitoring device
Fresh concrete must also be protected against wind. The use of insulating coatings for this purpose is excellent.
The final conclusion:
Concrete placement in cold weather has many challenges, so it is important to deal with each problem in principle. Also, it is essential that all personnel be prepared to deal with the cold and use appropriate clothing and equipment. Concrete placement is recommended in the middle of the day, especially at noon when the temperature is higher than other hours. Other precautions are described in detail above.