What is a foundation?
What is Foundation:
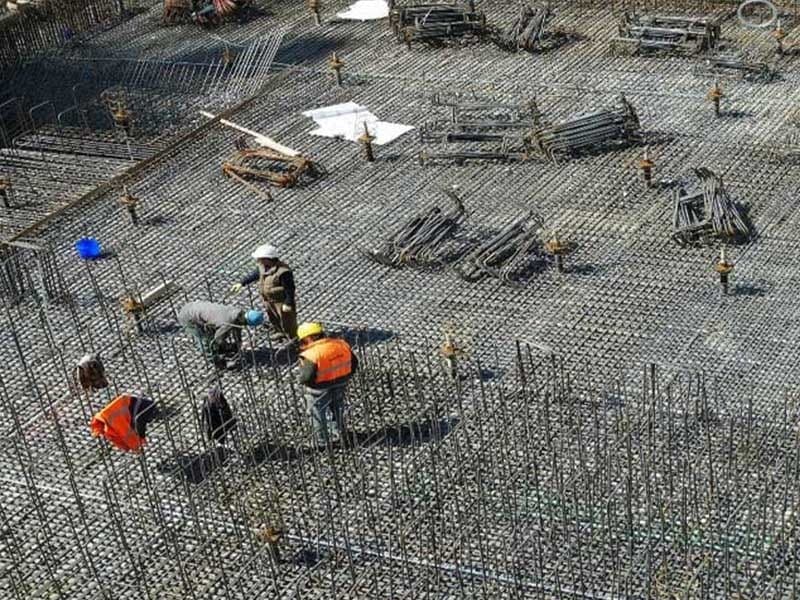
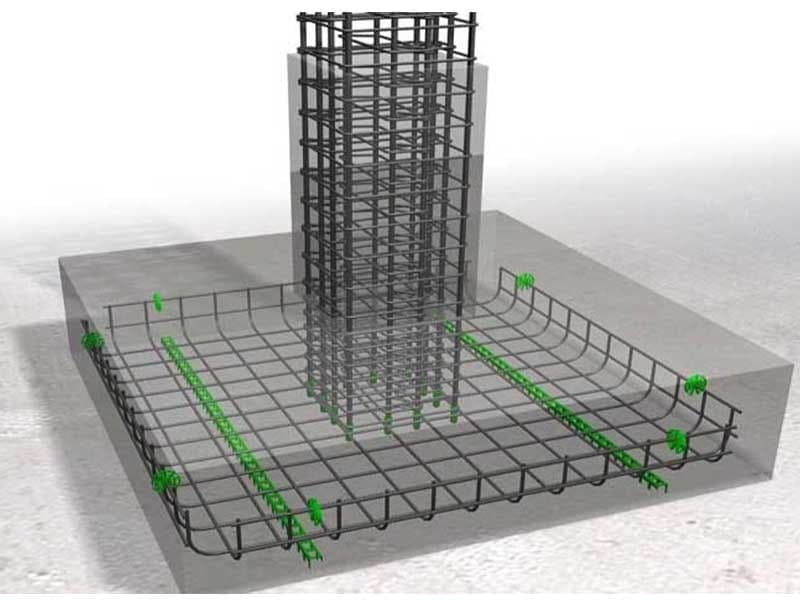
Foundation is the lowest and yet the most important part of a building which is in direct contact with the soil and transfers loads from the structure to the soil. Generally, the foundation can be divided into two groups: shallow and deep. The shallow foundation transfers the loads to a superficial layer of the soil, and the deep kind transfers the load to the deepest part of the soil. Stick with us for achieving a better understanding of the foundation.
The importance of the foundation in a building:
Foundations support the structure and transfer its load into soil or rock layers with sufficient carrying capacity and proper deployment features for supporting the structure.
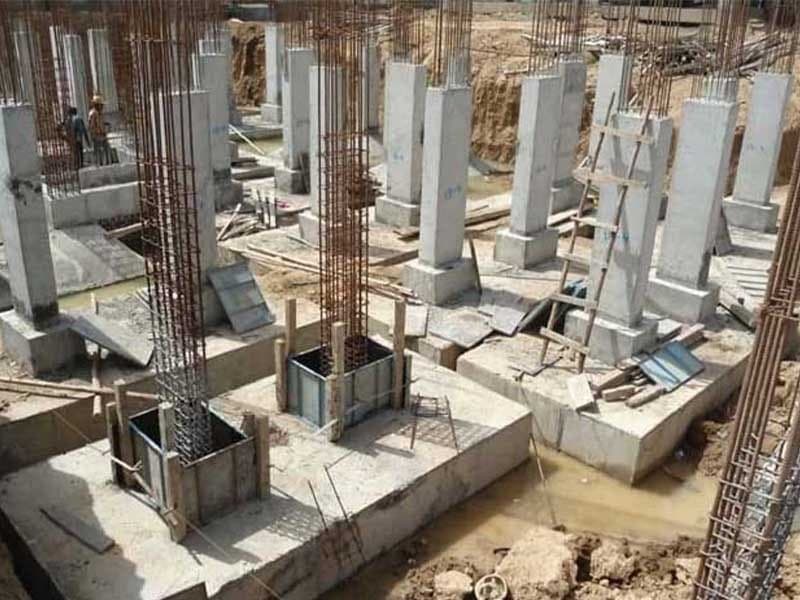
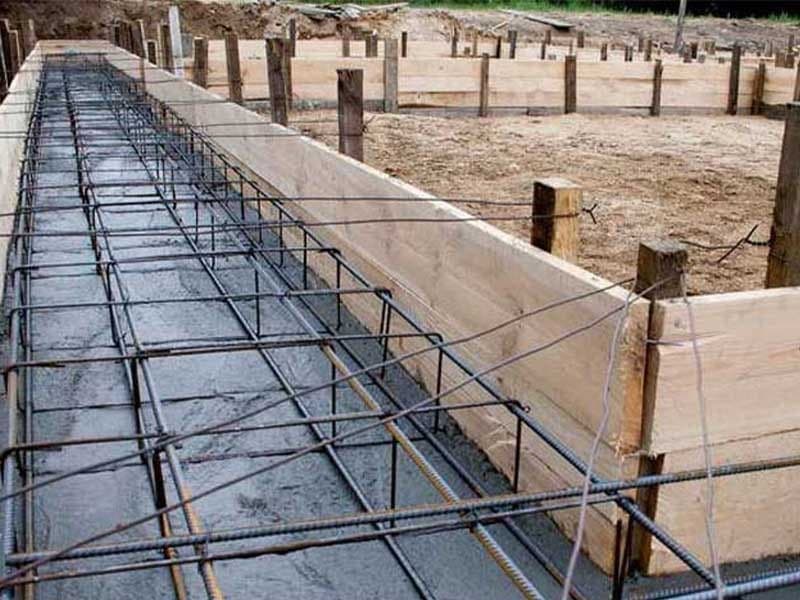
First, we need to reach a solid layer of soil for the foundation construction. For that, we need to excavate the land and ensure the soil’s solidity through experimental tests. After that, with formatting and placing longitudinal and transverse armatures, we begin concreting the foundation.
After the hardening of the concrete, the construction process of a structure can be started within a few days. In the past. Bricks, rocks, and mortar were used instead of concrete. The materials used to construct a foundation are dependent on the amount of load it will carry and the type of soil under the structure.
For designing a foundation, we need to be vigilant about its effects on the area around it. For example, the excavation and pilling for a deep foundation can lead to an undesired error in the soil and the foundation of a nearby structure. These things can sometimes cause danger to the surrounding buildings. These kinds of effects must be studied before the foundation-constructing process.
The base of each building is designed in a way to include the following:
- The soil underneath the structure should not undergo shear failure.
2. The settlement of the building must be within the permitted limit while we apply the service load.
3. The permitted pressurizing resistance can be considered as the amount of pressure that the soil can carry without failure.
The purpose behind implementing foundation:
Foundations are used for the following purposes:
- The foundation is the main reason for stability in each structure. A stronger foundation leads to a more stable structure.
2. Proper design for implementing foundations creates a suitable and solid platform for developing the infrastructure on it.
3. The foundation prevents the extra movements of the soil.
4. A good foundation can distribute the load evenly. This even transfer helps to prevent uneven movements of the building. Differential settlement is a bad construction effect that needs to be in the attention of the accounting engineer.
5. The foundation is used for the complete distribution of load from the structure into a large surface and then into the underneath soil. This transferred load must be within the tolerance limit of the soil.
The main functions of the foundation can be known as follows:
- Provides the general lateral stability of a structure.
2. Foundation is in the service of providing a surface for implementing the infrastructure.
3. Evenly distributes the load.
4. The intensity of the load is reduced for it to be within the safe tolerance capacity of the soil.
5. It resists in front of soil movement and holds the building still.
6. Scouring (as a result of water flow) and other issues related to the land’s humidity are partly solved by implementing a foundation.
The main kinds of foundations:
In the world of structural engineering, there are two certain groups for designing a foundation in buildings which are:
-
Shallow Foundation:
As the name suggests, these foundations have low depth. Their depth-to-width ratio is equal to or lower than one. They are more financially suitable than deep foundations since they need less drilling because the shallow foundations are usually implemented in the solid layers which are considerably close to the surface of the land.
-
Deep Foundations:
When there is a need for reaching strong grounds, a deep foundation is necessary. These foundations are usually used in places in which the soil does not have a sufficient loading capacity, the water levels are higher, there are high settlements of the soil, and technically, areas with soft natural soil. The most common types of foundations are the ones with piles. Piles are commonly used for reaching solid layers of the soil.
Types of shallow foundation:
We will point out the types of shallow foundations in the following:
Isolated Footing:
The isolated footing is the most common and widely used kind amongst the foundations. It is usually known as a square, rectangular, or circular-shaped concrete and is implemented for each column. This foundation is a suitable choice for lightweight structures such as small residential buildings with a low number of floors and no risk of seismicity.
Combined Footing:
The combined footing is used to support more than one column. This can be done only when the columns are near together. To design a combined footing, the center of the foundations must coincide with the combined load of each footing. Therefore, the soil’s bearing pressure is evenly distributed underneath the footing to prevent uneven settlements of the soil.
Bascule Footing:
This footing is constructed from two concentric individual foundations which are connected by a chain. This footing is suitable when the columns are far from each other or when a load of an extra-axial column is applied to the foundation. The chain must be a rectangular beam that is placed between two columns. The width of the chain is usually equal to the width of the largest column plus an extra 100 millimeters and its depth is determined due to the maximum bending moment.
Strap Footing:
The strap footing is built with a continuous structure with generally supports the columns in X and Y directions. It can also be used when a few columns are placed along each other and there is a very small space between them. Nowadays, the strap foundation is the most popular foundation used in common urban buildings. The design of the strap and other kinds of footing is done by the SAFE application.
Mat Foundation:
The mat foundation is a thick footing that is used for bearing a whole weight of a structure. This kind of foundation is used when the load of the column is heavy and when the load-bearing capacity of the soil is very low. The mat foundation can also be used for tall or sensitive structures if the load-bearing pressure of the soil can tolerate the bearing pressure caused by the overall load of the structure.
Types of deep foundation:
The deep foundations are divided as follows:
-
Driven Pile:
The driven piles are driven to the ground by the vibration of hammers and special tools. They are made of pre-made, concrete or steel piles (H-Beam) or pipe-shaped steel piles with a capacity of 800 to 3000 kilonewtons. Even though these piles are cheap and easy to install, implementing them needs a lot of caution and attention in matters of safety. Controlling the noises while using this pile is a challenge in itself and it is not advised for the soils which generally consist of hard rocks.
-
Mini Pile:
The mini piles are drilled piles with a small diameter that are used in limited spaces and have poor accessibility. They can tolerate up to 1000 kilonewtons of loads. They are usually made in the size of 0.3 meters in diameter and use a platform that is usually less than 2 meters in height.
-
Bored Pile:
This may be the most common type of deep foundation used in construction. Pre-drilling is used based on the place in which the pile is going to be implemented. A covering and bentonite system is necessary to stabilize the borehole. The bored pile is a definite choice for tall buildings and sensitive projects.
Requirements for implementing a foundation:
The design and construction of a well-functioning foundation have to be done according to some requirements that are as follows:
- Designing and construction of a foundation are done in such a way that it can cause stability and also transfer the dead load and the imposed loads into the soil. This transfer needs to be done without any settlement and this can lead to some permanent issues for the structure.
2. By having a firm and solid base for the foundation we can stop different kinds of settlements from occurring. This feature is illustrated in areas in which the service loads are not naturally uniform.
3. According to the area and the soil, it is usually advised that a deeper construction is implemented so that it could prevent any kind of long-term damage. These damages are generally caused by shrinkage and swelling which are the results of temperature changes.
4. The foundation should be placed somewhere which would not undergo any heavy construction in the future.
How does designing a foundation work?
Designing a foundation is creating a construction plan for making a solid platform or base for a building. This function is specialized and is usually done by a structural engineer. Foundation is the base of the structure that is placed on the ground and it supports the rest of the building. Therefore, foundational designing has to be consisted of studying the ground underneath the foundation and the materials used in making it. In foundational designing, you need to pay attention to the things below:
The depth of the foundation:
There are different kinds of building foundations. Except for slab foundations which are placed on the ground, most of the foundations are installed in different depths under the ground. The needed depth for each foundation is depended on various things like:
A) The bearing capacity of the soil: This determines how much load should a certain soil tolerate.
B) The type of soil: Different kinds of soil have different features that can play a role in their suitability for supporting a foundation.
C) Depth of freezing: The depth of the ground which freezes in the coldest time of the year is called freezing depth or cold line
D) Underground water table: an underground water table could limit the depth of the foundation in addition to the materials that can be used in it. The height of underground water is usually considered in a soil study.
E) The minimum depth: By ignoring other factors, the minimum depth of a foundation is generally not lower than 75 centimeters.
The materials used in the foundation construction:
Foundations are usually made of rocks, bricks, and concrete. Construction materials have high-pressure resistance and they are more resistant to humidity and soil in comparison to wood and steel. A stone or brick-made foundation is usually extended onto the surface of the ground to protect the other constructional materials from humidity and other kinds of damaging effects of touching the ground.
These foundations are usually reinforced by armatures. Contractors often use hydraulic cement to seal around the pipes. The most important material for constructing a foundation is reinforced concrete. This material is now being used in different scales in most projects,3, especially in earthquake-prone areas with weak-based soil.
Load-transferring of the foundation:
Foundations have to be designed in such a way as to evenly transfer the imposed load of the building to the soil. These loads are the total of dead loads, live loads, and side loads. The pure loading capacity imposed on the soil should not go over the soil’s tolerance capacity.
In foundation designing you also need to consider the building’s stability to control all the side movements to prevent any damage to the structure. In addition, the general layout of the foundation and the land’s features need to be studied to understand and implement different structural strategies.
Conclusion:
A building needs a foundation to transfer its load from the highest to its lowest point. Different kinds of foundations need to be chosen according to the amount of load imposed on the ground, the conditions of land and soil, the probable existence of underground water, having enough space, sensitivity to sound and vibration, and other things. In any case, the foundation has to be designed based on the needs of the project and the conditions of the soil.